Nowadays, heart disease is one of the leading causes of death.
Most often, cardiovascular problems occur in people over 50,
however, the modern way of life, far from optimal, deteriorating environmental situation, constant stress, poor nutrition, etc. includes younger people at risk.
The heart is a powerful pump that circulates blood. With the circulating blood, the organs and tissues receive nutrients and oxygen, without which their vital activity would be impossible.
To carry out this significant work, the heart needs a large amount of oxygen, which is responsible for the delivery of an extensive system of coronary arteries. Pathological changes in the condition of blood vessels invariably lead to a deterioration of the blood supply to the heart and, as a consequence, to the development of serious cardiovascular diseases.
Atherosclerosis is the most common chronic disease that affects the arteries.
Gradually growing atherosclerotic plaques on the inner lining of the vascular wall, single or multiple, are mainly cholesterol deposits. Growth in the artery of connective tissue (sclerosis) and calcification of the vessel wall lead to slowly progressive deformation, narrowing of the lumen to complete obstruction (obliteration) of the artery and thus cause chronic, slowly increasing insufficiency of blood supply to the organ feeding through the affected artery.
In the case of the heart muscle, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- chest pain
- nausea
- shortness of breath
- tachycardia
- excessive sweating
Cardiologists have many advanced methods of surgical treatment.
Prior to the advent of intravascular therapy, the only surgical treatment for coronary heart disease was coronary artery bypass grafting (creating a shunt to bypass a narrowed area of a blood vessel).
Many patients are now able to avoid surgery through the use of effective and low-trauma methods, one of which is coronary stenting (coronary stent implantation). But first you need to be examined to know exactly the condition of the vessels of the heart. The most accurate method of diagnosis today is coronary angiography - the "gold standard" for diagnosing coronary heart disease worldwide.
Coronary angiography is an X-ray contrast method of vascular examination, which detects the location and extent of their damage.
This type of study is the most accurate and reliable way to diagnose coronary heart disease and allows you to decide on the need for medical procedures such as angioplasty and stenting.
This procedure is invasive, as it involves the introduction of a special catheter and can be performed both for diagnostic purposes and to monitor certain operations.
Indications for coronary angiography:
- detected or suspected coronary heart disease
- chest pain
- myocardial infarction
- preparation for heart disease surgery
- in heart failure
- in cases of risk in non-invasive studies with load
- angina pectoris in ventricular arrhythmias
- in cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- with ischemic pulmonary edema
Indications for coronary angiography are determined by the attending physician, who prescribes the necessary tests and examinations, which include:
-general blood test
- blood type
- Rh factor
- tests for hepatitis B and C, HIV, RW
- electrocardiography (ECG) in 12 leads
- echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart)
In addition to these, additional studies may be assigned.
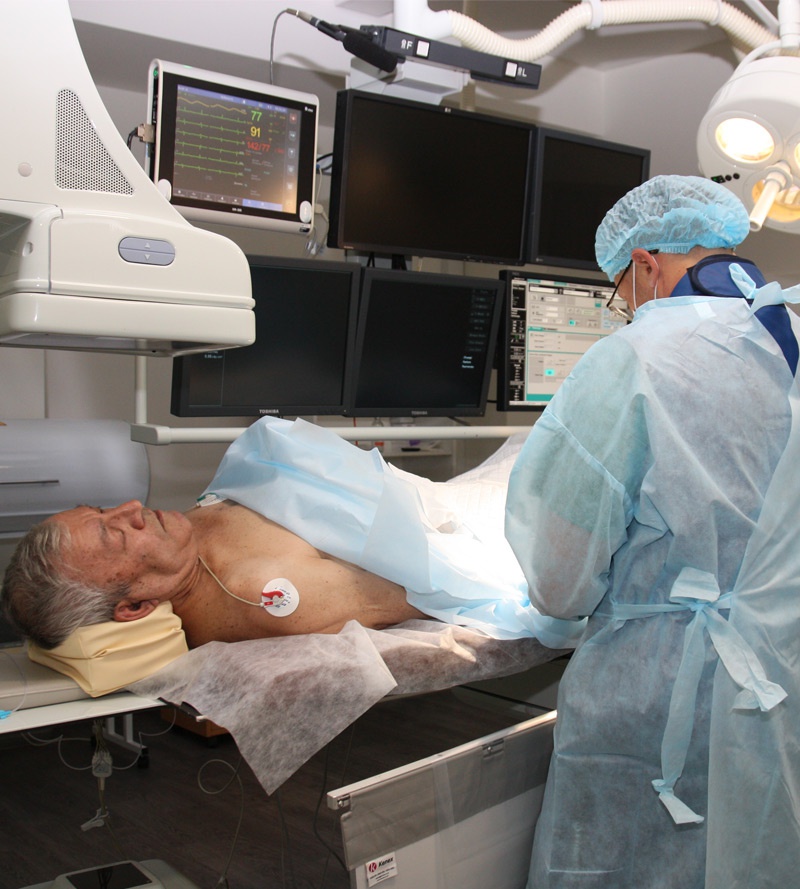
The coronary angiography procedure takes place in the X-ray endovascular surgery room.
After anesthesia, the study begins - a special catheter is passed through the femoral artery into the upper part of the aorta into the lumen of the coronary arteries. In some cases, a catheter may be inserted through the forearm artery.
With the help of a catheter, an X-ray contrast agent is injected into the blood, which is carried by the bloodstream through the coronary vessels, making their condition visible on a special device - an angiograph. Coronary angiography determines the degree and extent of coronary artery disease, which determines further treatment tactics.
This procedure is minimally invasive, which eliminates the need for general anesthesia, so it is performed under local anesthesia.
Coronary angiography allows simultaneous balloon dilatation and stenting.
In this case, the doctor's decision will be agreed with the patient.
However, the following complications are possible:
- bleeding at the puncture site
- arrhythmia
- allergic reaction to contrast
- coronary artery thrombosis
- acute dissection of the intima artery
- development of myocardial infarction
Usually,if you follow the doctor's recommendations, the risk of complications is almost absent.
In case of their occurrence, the qualification of the medical staff, the experience of specialists and the appropriate equipment allow to provide appropriate emergency care.
Coronary angiography results allow cardiologists to assess the condition of the heart vessels and recommend options for further treatment, medication, stenting or shunting (open heart surgery).
| Doctor | Name | Specialization | Reception time (Sunday) |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Kamyanchenko Vyacheslav Nikolaevich | Anesthesiology, Cardiology | - |
